No one likes to spend money, and everyone on the Cisco 300-410 exam loves the most cost-effective Cisco ENARSI online resource. We have updated the Cisco 300-410 dumps that meet the requirements. This fact explains why so many people seek the Cisco ENARSI online resource 300-410 dumps to help them pass the exam.
The 300-410 dumps are good research material for the Simplifying Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) exam, and the 300-410 dumps provided by Pass4itSure, in particular, are the most cost-effective.
Go to the Pass4itSure 300-410 dumps page: https://www.pass4itsure.com/300-410.html you’ll see three options (PDF Only: $45.99, Software Only: $49.99, Software + PDF: $59.99) and choose the one that fits your budget to start learning.
There’s a truth to tell you, “If you want to, you have to give something.” This means that you need a lot of practice. Constantly improve your exam skills in practice, using 300-410 dumps of question answers.
Preparing for the Cisco ENARSI 300-410 Exam Choose The Most Cost-effective Online Resource, Premise?
First of all, you must first understand the basics of the 300-410 exam:
Abbreviation: Cisco ENARSI
Full name: Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
Certification: CCNP
Official Cisco training: Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
Exam duration: 90 minutes
Cost: $300, (plus tax or use Cisco Learning Credit)
Languages: English and Japanese
Topic (Cisco ENARSI)
- Layer 3
- VPN services
- Infrastructure security
- Infrastructure services
- Infrastructure automation
Apart from that, you also need to know about CCNP Enterprise certification (Cisco Certified Specialist – Enterprise Advanced Infrastructure Implementation).
To earn CCNP Enterprise, you pass two exams: a core exam and an enterprise concentration exam of your choice. 300-410 ENARSI is a class of concentration exams, and not only do you pass it, but you also need to pass the core exam 350-401 ENCOR to fully earn the CCNP Enterprise certification.
Do you want a free dumps of the Cisco ENARSI 300-410?
300-410 dumps are often the required resources for Cisco ENARSI exams. Below, I will share with you:
Free: Cisco 300-410 Dumps Practice Test (PDF) Online Resource
QUESTION 1
Which command should be executed on all ABRs in an area to configure it as a totally stubby area?
A. Router(config-router)# area process-id stub [no-summary]
B. Router(config-router)# area area-id [no-summary] stub
C. Router(config-router)# area area-id stub [no-summary]
D. Router(config-ospf)# area router-id [no-summary] stub
Correct Answer: C
The correct syntax for the area stub command to configure a totally stubby area is shown below:
Router(config-router)# area stub [no-summary] Note that the optional no-summary keyword is used only on area border routers (ABRs) to block summary link advertisements into the stub area. This option creates a totally stubby area. All internal routers in the area need only the stub keyword without the no summary keyword.
It is very important to configure the command consistently on all routers within the area. OSPF sends its stub status (on or off) in its hello packets. If two neighbors have conflicting stub status, for example, if one indicates that a stub is present and the other indicates that no stub is present, they will not form an adjacency, and you end up with no OSPF communication over that link.
The other options are either using incorrect syntax or being executed at an incorrect prompt. The area stub command should be executed at the OSPF router configuration prompt.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify network types, area types, and router types
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > What Are OSPF Areas and Virtual Links? > What Are Areas, Stub Areas, and Not-So-Stubby Areas? Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference > area stub
QUESTION 2
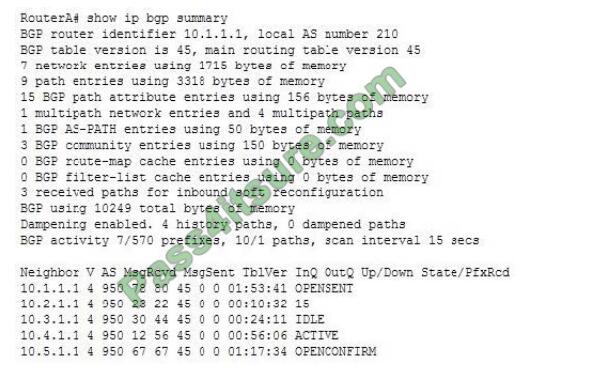
Consider the following output of the show ip bgp summary command: Which of the following neighbors have an established connection with RouterA?
A. 10.1.1.1
B. 10.2.1.1
C. 10.3.1.1
D. 10.4.1.1
E. 10.5.1.1
Correct Answer: B
The neighbor with the IP address 10.2.1.1 has an established connection with RouterA. This is because the
State/PfxRcd value for this neighbor is a number, 15, which indicates the number of prefixes received by RouterA from the neighbor.
The prefixes are exchanged between BGP neighbors through the update message, which can be transmitted only if an established connection exists between the neighbors. An established connection exists between two neighbors if the local router is in Open Confirm state and it receives a KEEPALIVE or an UPDATE message.
The connection between RouterA and the neighbor with the IP address 10.1.1.1 is not established. This is because the State/PfxRcd value for this neighbor is OPENSENT. In this state, RouterA sends an OPEN message to a neighbor to determine the parameters for establishing a connection. The OPENSENT state occurs before the connection is established.
The connection between RouterA and the neighbor with the IP address 10.3.1.1 is not established. This is because the State/PfxRcd value for this neighbor is IDLE. In this state, RouterA does not accept any incoming connections from the neighbor.
The connection between RouterA and the neighbor with the IP address 10.4.1.1 is not established. This is because the State/PfxRcd value for this neighbor is ACTIVE. In this state, RouterA is attempting to establish a BGP peering session but it is not yet complete.
The connection between RouterA and the neighbor with the IP address 10.5.1.1 is not established. This is because the State/PfxRcd value for this neighbor is OPENCONFIRM. In this state, RouterA waits for a KEEPALIVE or NOTIFICATION message from the neighbor.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe, configure, and verify BGP peer relationships and authentication
References:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip bgp summary
QUESTION 3
Refer to the exhibit.
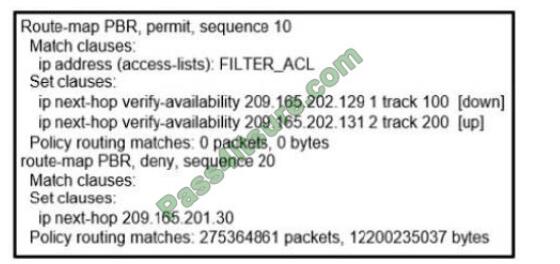
An engineer has configured policy-based routing and applied the configuration to the correct interface. How is the configuration applied to the traffic that matches the access list?
A. It is dropped
B. It is forwarded using the routing table lookup
C. It is sent to 209.165.202.131.
D. It is sent to 209.165.202.129.
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 4
Which show command displays the status of all of a router\’s Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) connections in a concise format?
A. show ip bgp
B. show ip bgp summary
C. show ip bgp connections
D. show ip bgp neighbor\’s summary
Correct Answer: B
The correct answer is show ip bgp summary.
Although show ip bgp neighbors will show you the status of your connections to neighbors, only show ip bgp summary shows it to you in a concise, summarized format, with one neighbor listed per line. It displays both iBGP and eBGP neighbors and the number of prefixes that have been learned from the neighbor.
Below is an example of the output of the show ip bgp summary command:
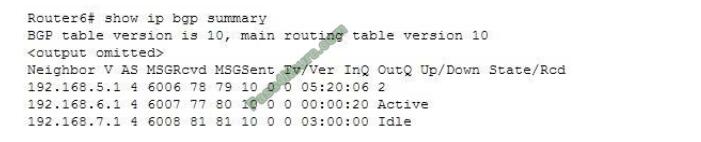
The following information can be obtained from this output:
The BGP session to 192.168.5.1 is established. A number in the State column indicates that the session is established. This number indicates the number of prefixes received from the neighbor. Router6 is attempting to establish a BGP peering session with the 192.168.6.1 neighbor. This is indicated by the keyword Active in the State column.
Several show commands can be used to verify BGP configuration and operation:
show ip bgp – displays the contents of the BGP routing table show ip bgp summary – displays the status of BGP connections in a summary format show ip bgp neighbors – displays information about the TCP and BGP connections to neighbors
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe, configure, and verify BGP peer relationships and authentication
References:
Cisco IOS Master Command List, Release 12.4 > a through b > BGP > Commands: show ip through T > show ip bgp summary
QUESTION 5
What are two functions of IPv6 Source Guard? (Choose two.)
A. It works independent from IPv6 neighbor discovery.
B. It denies traffic from unknown sources or unallocated addresses.
C. It uses the populated binding table for allowing legitimate traffic.
D. It denies traffic by inspecting neighbor discovery packets for specific patterns.
E. It blocks certain traffic by inspecting DHCP packets for specific sources.
Correct Answer: BC
IPv6 source guard is an interface feature between the populated binding table and data traffic filtering. IPv6 source guard can deny traffic from unknown sources or unallocated addresses.
QUESTION 6
A TFTP server, a DNS server, and a TACACS server are residing in the 192.168.5.0/24 subnet. Their IP addresses are 192.168.5.2, 192.168.5.3, and 192.168.5.4, respectively. You would like to configure the routers to forward UDP broadcasts to these servers.
Which of the following commands or sets of commands would configure this to occur using the LEAST number of commands?
A. ip helper-address 192.168.5.2 69 ip helper-address 192.168.5.3 53 ip helper-address 192.168.5.4 49
B. ip helper-address 192.168.5.2 ip helper-address 192.168.5.3 ip helper-address 192.168.5.4
C. ip helper-address 192.168.50 69 53 49
D. ip helper-address 192.168.5.255
Correct Answer: D
The only command required is ip helper-address 192.168.5.255. This command is a directed broadcast to the subnet on which the servers reside which will cause all servers to receive the broadcast. Each server will process only the packets aimed at the port on which they are listening.
It not necessary to specify any port numbers because the ip helper-address command will forward to the following ports by default:
NTP – port 37
TACACs – port 49
DNS – port 53
BootP – port 67
TFTP – port 69
NetBIOS Name server – port 137
NetBIOS Datagram server – port 138
While the following command set would work, it does not contain the least number of commands:
ip helper-address 192.168.5.2 69
ip helper-address 192.168.5.3 53
ip helper-address 192.168.5.4 49
It is not required to specify each server and its respective port number.
The following command set would also have the desired results, because port numbers are not required for the default services:
ip helper-address 192.168.5.2
ip helper-address 192.168.5.3
ip helper-address 192.168.5.4
However, this is not the least number of commands you can execute to achieve the solution.
The command ip helper-address 192.168.50 69 53 49 would not work because it is addressed to the network number of the subnet to which the servers are connected. To send to them all requires a directed broadcast.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify IPv4 and IPv6 DHCP
References:
Cisco Press > Articles > Cisco Networking Academy > CCNP 1: Advanced IP Addressing Management Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Application Services Command Reference > ip helper-address
QUESTION 7
Users were moved from the local DHCP server to the remote corporate DHCP server. After the move, none of the users were able to use the network.Which two issues will prevent this setup from working properly? (Choose two)
A. Auto-QoS is blocking DHCP traffic.
B. The DHCP server IP address configuration is missing locally
C. 802.1X is blocking DHCP traffic
D. The broadcast domain is too large for proper DHCP propagation
E. The route to the new DHCP server is missing
Correct Answer: BE
QUESTION 8
Refer to the exhibit.
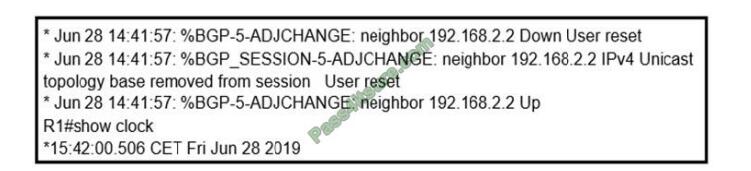
An engineer is troubleshooting BGP on a device but discovers that the clock on the device does not correspond to the time stamp of the log entries. Which action ensures consistency between the two times?
A. Configure the service timestamps log uptime command in global configuration mode.
B. Configure the logging clock synchronize command in global configuration mode.
C. Configure the service timestamps log datetime localtime command in global configuration mode.
D. Make sure that the clock on the device is synchronized with an NTP server.
Correct Answer: C
The Time zone needs to be changed. default it UTC Central European Time (CET)
https://community.cisco.com/t5/networking-documents/router-log-timestamp-entries-are-different-from-the-systemclock/ta-p/3132258
QUESTION 9
What would be a use case for the HSRP configuration below?

A. used to switch the active role to the other router in the HSRP group during a maintenance window
B. used to prevent this router from ever relinquishing the active role
C. used to prevent this router from ever performing the active role
D. used to allow preemption over multiple peers
Correct Answer: A
By tracking the loopback interface and decrementing the priority if it goes down, technicians would have a method of moving the active role to the other router by disabling the loopback interface. This method is less disruptive than disabling any of the physical interfaces. Although no decrement value has been specified, a default decrement of 10 will occur.
This configuration would not be used to prevent this router from ever relinquishing the active role. That would defeat the purpose of Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP), which is to provide failover by relinquishing the active role to the other router.
This configuration would not be used to prevent this router from ever performing the active role. That would defeat the purpose of HSRP which is to provide failover by this router taking the active role when there is an issue with the other router.
This configuration would not be used to allow preemption over multiple peers. When more than two routers are in an HSRP group, the active router is allowed preemption over multiple peers by default.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify tracking objects
References:
Home > Support > Technology support > IP > IP application services > Troubleshoot and alerts > Troubleshooting Technotes > How to use the standby preempt and standby track commands
QUESTION 10
What is a function of an end device configured with DHCPv6 guard?
A. If it is configured as a server, only prefix assignments are permitted.
B. If it is configured as a relay agent, only prefix assignments are permitted.
C. If it is configured as a client, messages are switched regardless of the assigned role.
D. If it is configured as a client, only DHCP requests are permitted.
Correct Answer: C
The DHCPv6 Guard feature blocks reply and advertisement messages that come from unauthorized DHCP servers and relay agents. Packets are classified into one of the three DHCP type messages. All client messages are always switched regardless of device role. DHCP server messages are only processed further if the device role is set to server.
Further processing of server messages includes DHCP server advertisements (for source validation and server preference) and DHCP server replies (for permitted prefixes). If the device is configured as a DHCP server, all the messages need to be switched, regardless of the device role configuration.
QUESTION 11
Refer to the following partial output of the show ip bgp neighbors command:

Which of the following can NOT be determined from the given output? (Choose all that apply.)
A. The ASN of rtrA
B. The ASN of 172.161.81.7
C. The best paths between rtrA and the 172.161.81.7 neighbor
D. The RID of the 172.161.81.7 neighbor
E. The status of the connection between rtrA and 172.161.81.7
Correct Answer: AC
The autonomous system number (ASN) of rtrA and the best paths between rtrA and the 172.161.81.7 neighbor cannot be determined from the given output.
The show ip bgp neighbors command displays the TCP and BGP connections from a given router to its neighbors. This command is executed in EXEC mode. You can use various optional keywords to view different aspects of the neighbors. For example, this command can display the details about a given neighbor, routes advertised to or received from neighbors, and the prefix-list received by neighbors.
In this case, the command is used to show the details about a specific neighbor of rtrA. The IP address (172.161.81.7) of the neighbor is provided in the command. The text BGP neighbor is 172.161.81.7 indicates the IP address of the neighbor.
The text remote AS 151 indicates that the neighbor is in the ASN 151. It can also be determined from the text external link that the neighbor is an eBGP neighbor. For iBGP neighbors, the text internal link will appear. The router ID (RID) of the neighbor can be determined from the text remote router ID 10.8.22.4.
The output also provides details about the state of the BGP connection, which is Established in this case. Furthermore, the duration for which the connection has been established, the duration for which BGP maintains neighbor relationship in the absence of messages, and the keepalive duration are also displayed.
The state of the connection between the local router (rtrA) and the given neighbor (172.161.81.7) can be any of the following: Idle Indicates that the local router does not accept any connection from its neighbor Idle (admin) Indicates that the connection between the two routers has been shut down administratively by using the neighbor shutdown command
Connect Indicates that the local router has already sent an connection request to its neighbor Active Indicates that the local router is listening for connection requests from the neighbor OpenSent Indicates that the local router has sent an OPEN message to its neighbor
OpenConfirm Indicates that the local router has received a KEEPALIVE or UPDATE message from its neighbor Established Indicates that a BGP connection has been successfully created between the local router and its neighbor
The status of the connection between two BGP neighbors can also be viewed by using the show ip bgp summary command, as shown below:

In the above output, it can be determined that the command router bgp 210 was executed on rtrA because the local AS is 210 in the output. It can be determined that the command neighbor 45.1.1.5 shutdown was issued on rtrA because the state of the neighbor relationship with the router at 45.1.1.5 is listed as IDLE(ADMIN).
All the other options are incorrect because the respective details are displayed by the show ip bgp neighbors command.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify eBGP (IPv4 and IPv6 address families)
References:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip bgp neighbors Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip bgp summary
QUESTION 12
Refer to the exhibit.
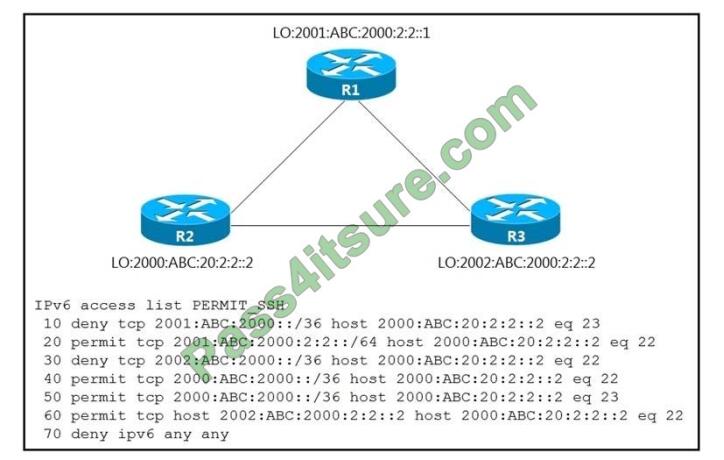
An IPv6 network was newly deployed in the environment and the help desk reports that R3 cannot SSH to the R2s Loopback interface. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Modify line 10 of the access list to permit instead of deny.
B. Remove line 60 from the access list.
C. Modify line 30 of the access list to permit instead of deny.
D. Remove line 70 from the access list.
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit. An OSPF neighbor relationship between R2 and R3 is showing stuck in EXCHANGE/EXSTART state. The neighbor is established between R1 and R2. The network engineer can ping from R2 to R3 and vice versa, but the neighbor is still down. Which action resolves the issue?
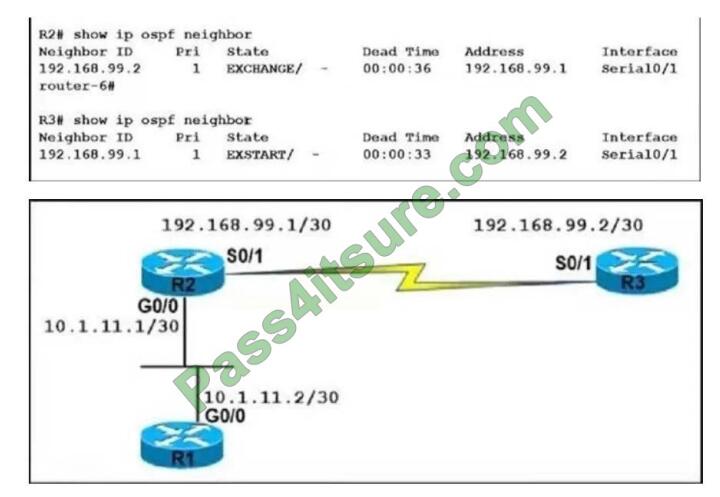
A. Restore the Layer 2/Layer 3 conectivity issue in the ISP network.
B. Match MTU on both router interfaces or ignore MTU.
C. Administrative “shut then no shut” both router interfaces.
D. Enable OSPF on the interface, which is required.
Correct Answer: B
For more 300-410 questions, you need to visit this website
Free 300-410 Dumps Download Online https://drive.google.com/file/d/1TYCJWmDmt8KJhz-HyWiovV7rxH45HVmX/view?usp=sharing
