Has anyone done the Microsoft 070-341 dumps? The Core Solutions of Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 (70-341 Exchange) exam is a 204 questions assessment in pass4itsure that is associated with the MCP, MCSE certification. “Core Solutions of Microsoft Exchange Server 2013” is the exam name of Pass4itsure Microsoft 070-341 dumps test which designed to help candidates prepare for and pass the Microsoft 070-341 exam. Best Microsoft 070-341 dumps exam video 204Qs&As Core Solutions of Microsoft Exchange Server 2013. Passing this exam along with the other two exams confirms that a candidate has the https://www.pass4itsure.com/70-341.html dumps skills and knowledge necessary for implementing, managing, maintaining, and provisioning services and infrastructure in a Windows Server 2012 environment.
[New Pass4itsure 070-341 Dumps PDF From Google Drive]: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0BwxjZr-ZDwwWczUzdm1LMWFPT0k
[New Pass4itsure 070-347 Dumps PDF From Google Drive]: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0BwxjZr-ZDwwWdkVZWTJKYnNWUzA
Latest and Most Accurate Pass4itsure 070-341 Dumps Exam Q&As:
Question No: 14 – (Topic 2)
You need to ensure that all of the email messages sent from the Internet to adatum.com are routed through the contoso.com organization. What should you create in contoso.com? (Each corrects answer presents part of the solution. Choose all that apply.)
A. a contact object for each adatum.com recipient
B. an internal relay accepted domain for adatum.com
C. a Send connector that is configured to point to the contoso.com transport servers
D. a Send connector that is configured to point to the adatum.com transport servers
E. an authoritative accepted domain for adatum.com
070-341 exam Answer: B, D
Explanation:
Internal Relay Domain
You can configure a relay domain as an internal relay domain or as an external relay domain. These two relay domain types are described in the following sections. When you configure an internal relay domain, some or all of the recipients in this domain don’t have mailboxes in this Exchange organization. Mail from the Internet is relayed for this domain through Transport servers in this Exchange organization. This configuration is used in the scenarios that are described in this section. An organization may have to share the same SMTP address space between two or more different messaging systems. For example, you may have to share the SMTP address space between Exchange and a third-party messaging system, or between Exchange environments that are configured in different Active Directory forests. In these scenarios, users in each email system have the same domain suffix as part of their email addresses. To support these scenarios, you need to create an accepted domain that’s configured as an internal relay domain. You also need to add a Send connector that’s sourced on a Mailbox server and configured to send email to the shared address space. If an accepted domain is configured as authoritative and a recipient isn’t found in Active Directory, a nondelivery report (NDR) is returned to the sender. The accepted domain that’s configured as an internal relay domain first tries to deliver to a recipient in the Exchange organization. If the recipient isn’t found, the message is routed to the Send connector that has the closest address space match. If an organization contains more than one forest and has configured the global address list (GAL) synchronization, the SMTP domain for one forest may be configured as an internal relay domain in a second forest. Messages from the Internet that are addressed to recipients in internal relay domains are relayed to the Mailbox servers in the same organization. The receiving Mailbox servers then route the messages to the Mailbox servers in the recipient forest. You configure the SMTP domain as an internal relay domain to make sure that the email that’s addressed to that domain is accepted by the Exchange organization. The connector configuration of your organization determines how messages are routed.
B An accepted domain is any SMTP namespace for which a Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 organization sends or receives an email. Accepted domains include those domains for which the Exchange organization is authoritative. An Exchange organization is authoritative when it handles mail delivery for recipients in the accepted domain. Accepted domains also include domains for which the Exchange organization receives mail and then relays it to an email server that’s outside the organization for delivery to the recipient.
D 2nd part of establishing an internal relay domain is to establish a Send Connector that is configured to point to the other organization’s mail servers (a datum)
NOTA
Better to establish an internal relay domain. A mail-enabled Active Directory contact that contains information about people or organizations that exist outside the Exchange organization. Each mail contact has an external email address. All messages sent to the mail contact are routed to this external email address.
NOT C
Need to establish a Send connector to adatum.com, not contoso.com
NOT E
Need to establish an internal relay domain not an authoritative accepted domain for adatum.com
Question No: 15 – (Topic 2) You need to prevent several users in the Miami office from establishing more than two concurrent Exchange ActiveSync connections to the Exchange Server organization. The solution must affect only the users in the Miami office. Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. Create a new throttling policy that has the Organization scope.
B. Create a new throttling policy that has the Global scope.
C. Create a new throttling policy that has the Regular scope.
D. Run the Set-ThrottlingPolicyAssociation cmdlet.
E. Run the Set-ThrottlingPolicy cmdlet.
F. Remove the default throttling policy.
Answer: C,D
Explanation:
New-ThrottlingPolicy
Use the New-ThrottlingPolicy cmdlet to create a non-default user throttling policy.
EXAMPLE 1
This example creates a non-default user throttling policy that can be associated with specific users. Any parameters that you omit inherit the values from the default throttling policy GlobalThrottlingPolicy_<GUID>. After you create this policy, you must associate it with specific users. New-ThrottlingPolicy -Name ITUserPolicy -EwsMaxConcurrency 4 -ThrottlingPolicyScope Regular The ThrottlingPolicyScope parameter specifies the scope of the throttling policy. You can use the following values. Regular Specifies a custom policy that applies to specific users. Organization Specifies a custom policy that applies to all users in your organization. Global Reserved for the default throttling policy.
C
Need to establish a New Throttling policy to limit the Exchange ActiveSync connections and that has a regular scope to associate with specific users.
D
Use the Set-ThrottlingPolicyAssociation cmdlet to associate a throttling policy with a specific object. The object can be a user with a mailbox, a user without a mailbox, a contact, or a computer account.
EXAMPLE 1
This example associates a user with a user name of the tony smith to the throttling policy ITStaffPolicy that has higher limits. Set-ThrottlingPolicyAssociation -Identity tony smith -ThrottlingPolicy ITStaffPolicy
NOTA
Need a regular scope
NOT B
Need a regular scope
NOT E
We need to associate the new throttling policy with respective users.
Use the Set-ThrottlingPolicy cmdlet to modify the settings for a user throttling policy.
EXAMPLE 1
This example modifies a throttling policy so that users associated with this policy can have a maximum of four concurrent requests running in Exchange Web Services.
NOT F
Need to create a new throttling policy
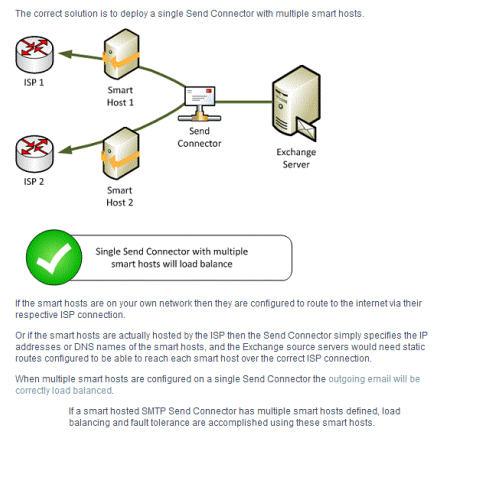
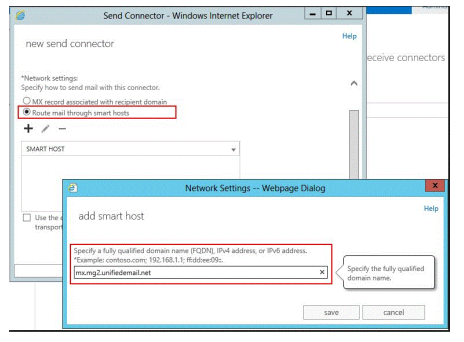
Question No: 16 – (Topic 2) You need to recommend a temporary solution to reroute all of the outbound email messages through the Miami mail appliance during the planned replacement of the New York mail appliance. What are the three possible ways to achieve the goal? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose three.)
A. Modify the value of the smart host of the Send connector in the New York office.
B. Increase the cost of the Send connector in the Miami office.
C. Increase the cost of the Send connector in the New York office.
D. Decrease the cost of the Send connector in the New York office,
E. Modify the value of the smart host of the Send connector in the Miami office.
F. Disable the Send connector in the New York office.
70-341 dumps Answer: A, C, F
Explanation:
Both Miami and New York have external connections to the internet with Client Access Servers In Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, a Send connector controls the flow of outbound messages to the receiving server
Internal Send connectors send e-mail to servers in your Exchange organization. This connector is configured to route e-mail to your internal Exchange servers as smart hosts. A smart host (also known as a relay host) is a server that redirects outbound mail. Send connectors to send e-mail to the Internet. This connector is configured to use Domain Name System (DNS) MX records to route e-mail. The cost is important if there is more than one connector that can be used, where the lower the cost the more preferred the route. This is useful if you have two Internet connections, and only want to use the slower one when the faster is down. Like weights in SRV records, the values are arbitrary. 1 vs 10 is no different than 1 vs 2, as long as there are no others you want to squeeze between them. Smart Host In some situations you may want to route email through a third-party smart host, such as in an instance where you have a network appliance that you want to perform policy checks on outbound messages. A smart host is a type of email message transfer agent which allows an SMTP server to route email to an intermediate mail server rather than directly to the recipient’s server. Often this smart host requires authentication from the sender to verify that the sender has privileges to have mail forwarded through the smart host. This is an important distinction from an open mail relay that will forward mail from the sender without authentication. Common authentication techniques include SMTP Authentication and POP before SMTP. When configured to be a backup mail server (not the primary MX record), a smart host configuration will accept mail on behalf of the primary mail server if it were to go offline. When the primary mail server comes back online, the mail is subsequently delivered via the smart host. Some ISPs, in an effort to reduce email spam originating at their customer’s IP addresses, will not allow their customers to communicate directly with the recipient’s mail server via the default SMTP port number 25. In this case, the customer has no choice but to use the smart host provided by the ISP. When a host runs its own local mail server, a smart host is often used to transmit all mail to other systems through a central mail server. This is used to ease the management of a single mail server with aliases, security, and Internet access rather than maintaining numerous local mail servers.
NOT B
Need to increase the cost of the Send Connect in the New York Office
NOT D
Need to increase the cost not decrease the cost of the Send Connector in the New York Office
NOT E
Need to modify the value of the smart host of the Send connector in the New York office
A
Modify the value of the smart host of the Send connector in the New York office to point to the smart host in the Miami office.
C
Increasing the cost of a Send Connector in the New York Office will make the Miami connection to the internet the most preferred outbound connection.
F
Disabling the Send connector in the New York Office will make the Miami connection to the internet the only outbound connection.
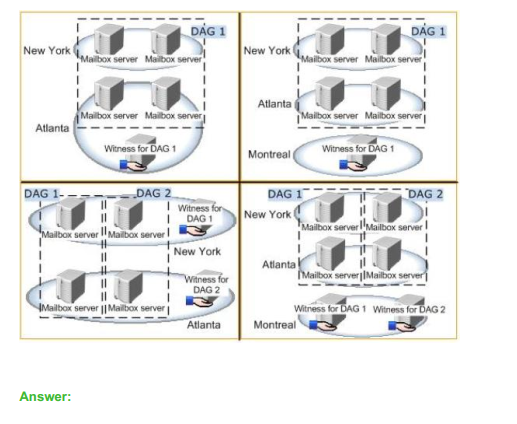
Question No: 17 HOTSPOT – (Topic 2) You are evaluating a DAG design for the New York and Atlanta offices. You need to ensure that all of the users in the New York and Atlanta offices can access their mailbox if the WAN link fails. Which DAG design should you deploy? To answer, select the appropriate DAG design in the answer area.
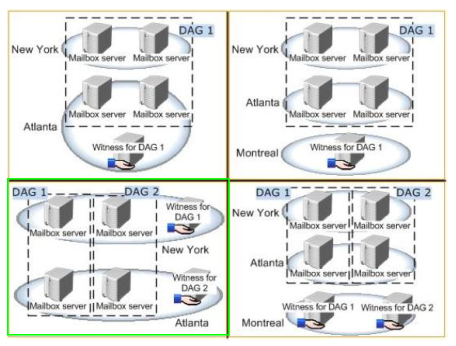
This 070-341 dumps exam is part one of a series of three exams that test the skills and knowledge necessary to implement a core Windows Server 2012 infrastructure in an existing enterprise environment. “Core Solutions of Microsoft Exchange Server 2013”, also known as 070-341 exam, is a Microsoft certification that covers all the knowledge points of the real Microsoft exam. Pass4itsure Microsoft 070-341 dumps exam questions answers are updated (204 Q&As) are verified by experts. The associated certifications of 070-341 dumps are MCP, MCSE. Passing this https://www.pass4itsure.com/70-341.html exam validates a candidate’s ability to implement and configure Windows Server 2012 core services, such as Active Directory and the networking services.
